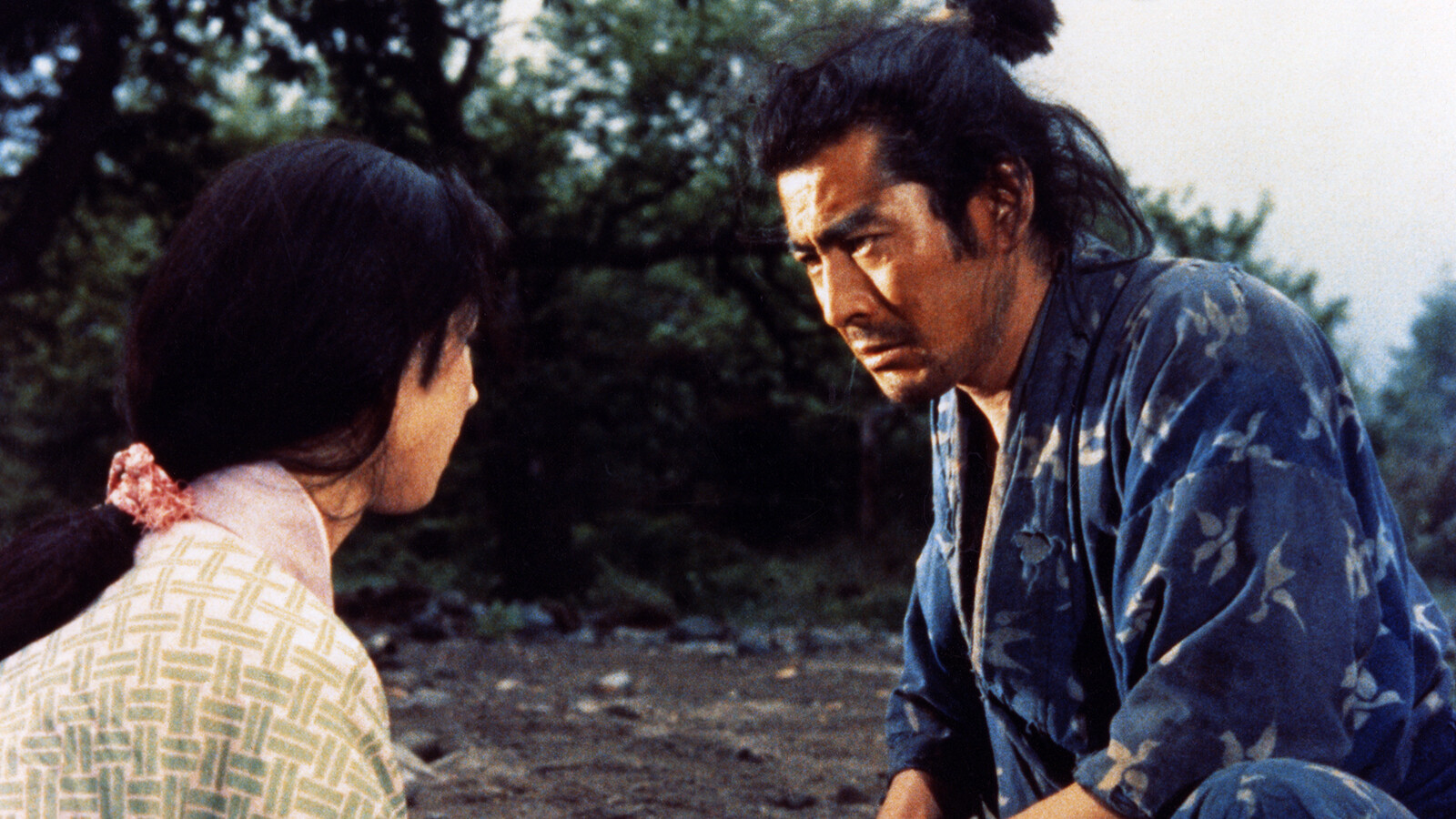
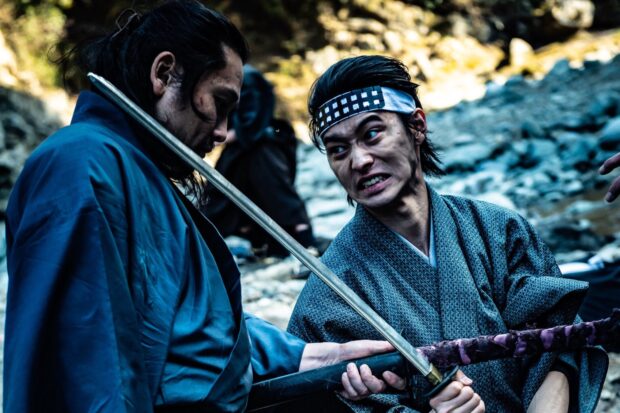
Sword Master and Wordsmith Miyamoto Musashi: Samurai, Artist, and Philosopher
 Miyamoto Musashi: The Unparalleled Master of Samurai Art
Miyamoto Musashi: The Unparalleled Master of Samurai Art
Miyamoto Musashi, recognized as one of the greatest samurais in Japanese history, symbolizes strength, skill, and a philosophy of life imbued with the tradition of honor. His life, spanning the early Edo period (17th century), was a time of change and challenges in which Musashi excelled as an unrivaled master of the sword, philosopher, and artist. His legend has survived through the centuries, and his teachings in the famous "Book of Five Rings" continue to inspire not only contemporary martial arts practitioners but also leaders and thinkers worldwide. Musashi's character, embodying the quintessence of the samurai spirit, transcends the confines of time, continuing his legacy in Japanese culture through numerous adaptations in anime, manga, and video games, remaining a constant source of inspiration and fascination.
Biography of Miyamoto Musashi
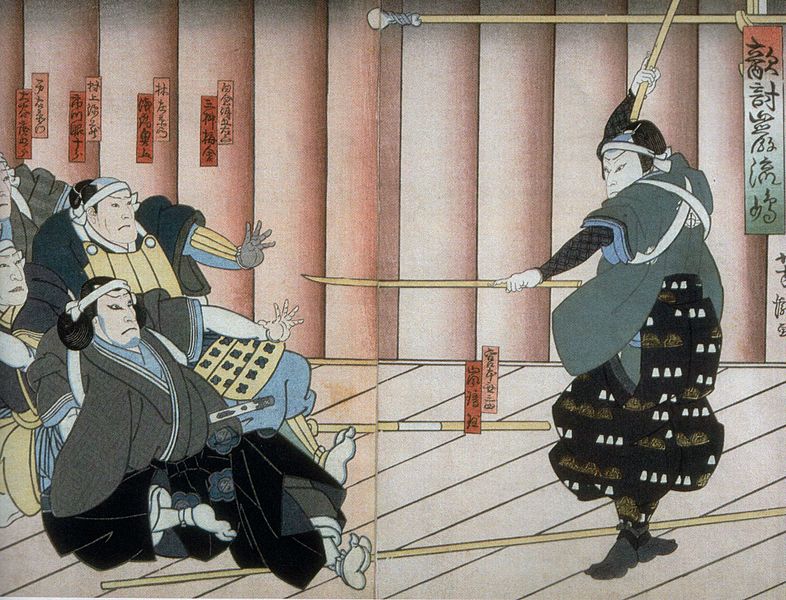
 Key Moments in His Samurai Career - Youth
Key Moments in His Samurai Career - Youth
During his travels, Musashi participated in numerous duels, honing his skills and gaining fame. His journeys took him to places like Kyoto, where in 1604, he fought a famous duel with the master of the Yoshioka school, Yoshioka Seijūrō. This duel, won by Musashi, solidified his reputation as an undefeated warrior. In 1605, he faced and defeated the lance master Musō Gonnosuke. However, the most legendary of Musashi's duels was with Sasaki Kojirō in 1612 on the island of Funajima. Musashi won using a wooden sword he had carved from an oar, symbolizing his creativity and unconventional approach to combat.
Adult Life and Later Career
Following these events, Musashi began to distance himself from the life of a samurai and focused on refining his philosophy and art. In 1641, he wrote "The Book of Five Rings" ("Go Rin No Sho")
 Significant Duels and Battles
Significant Duels and Battles
Miyamoto Musashi, known for his duels, often engaged in fights that significantly impacted his reputation and style of combat. One of the most significant was his confrontation with the Yoshioka clan, masters of swordsmanship in Kyoto. After defeating Yoshioka Seijūrō, Musashi faced his brother, Yoshioka Denshichirō, in a second duel, which he also won, ending the Yoshioka family's dominance in the region. Another key moment in his career was the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600, where Musashi fought for the Western army, which ultimately lost. Although he didn't achieve personal success in this battle, it profoundly influenced the shaping of his life and philosophy. The Battle of Sekigahara, a pivotal moment in Japanese history, prompted Musashi to reflect deeper on the nature of war and the samurai's life. This defeat and the resulting shift in power in the country inspired him to seek deeper meaning in martial arts and personal development, ultimately leading to the creation of his famous "Book of Five Rings."
 Duel of Strength and Cunning – Sasaki Kojirō
Duel of Strength and Cunning – Sasaki Kojirō
The duel with Sasaki Kojirō is considered the climax of Musashi's career and one of the most iconic events in Japanese combat history. The encounter took place on April 13, 1612, on the remote island of Ganryū. Kojirō, known for his long sword "Drying Pole" (Monohoshi Zao) and the "Swallow Cut" technique, was regarded as one of the finest swordsmen of his time. Musashi, known for punctuality, intentionally arrived late for the duel, disorienting and angering Kojirō as part of his psychological strategy.

This duel not only solidified Musashi's reputation as an undefeated warrior but also became a symbol of his creativity, cunning, and deep understanding of combat strategy. This duel has been frequently depicted in Japanese art, literature, and popular culture, becoming an integral part of Musashi's legend.
 The Transformation from Warrior to Philosopher
The Transformation from Warrior to Philosopher
Following his legendary duel with Sasaki Kojirō in 1612, Miyamoto Musashi gradually began distancing himself from the life of a samurai warrior. His transformation into a philosopher and artist was gradual and reflected the deep impact of his youthful experiences. Around 1614, during the Siege of Osaka, where he served in the Tokugawa army, Musashi began to ponder the purpose and consequences of the warrior's path more intensely. This experience, combined with the overall climate of change in the Edo period, when Japan transitioned from a state of constant war to peace, encouraged Musashi to seek a deeper meaning in life and art.
After leaving life at the courts and in the military, Musashi chose to live as a hermit. Around 1640, he settled in the Reigandō cave near Kumamoto on Kyushu, where he dedicated himself to writing, meditation, and art. In this seclusion, he wrote his most famous work, "The Book of Five Rings" ("Go Rin No Sho"), in which he compiled his thoughts on strategy, combat, and philosophy.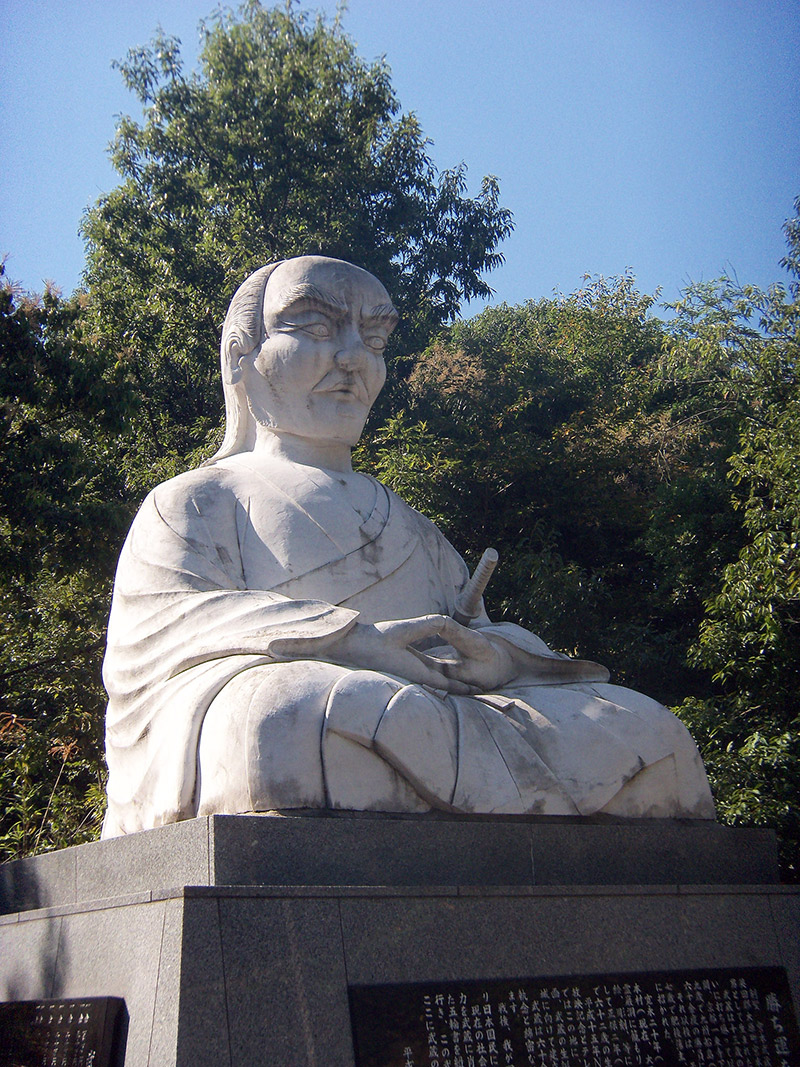 
The Works and Philosophy of Musashi
"The Book of Five Rings" - An Overview "The Book of Five Rings" ("Go Rin No Sho"), written by Miyamoto Musashi around 1643, is considered one of the most important Japanese works on combat strategy and life philosophy. Divided into five parts, each representing a "ring" or element – Earth, Water, Fire, Wind, and Void – the book is both a practical guide to swordsmanship and a deep meditation on the path of the warrior, known as "Bushidō." Musashi merges his experiences as a warrior with Zen philosophy, presenting a unique perspective on combat and life.
 Earth: The Foundations of Strategy The first part, "The Book of Earth," lays the foundation for the rest. Musashi discusses the basics of strategy and combat, emphasizing the importance of stability, understanding one's environment, and adapting to conditions. He also highlights the importance of harmony between body, mind, and spirit, crucial for achieving mastery in martial arts and in life.
Earth: The Foundations of Strategy The first part, "The Book of Earth," lays the foundation for the rest. Musashi discusses the basics of strategy and combat, emphasizing the importance of stability, understanding one's environment, and adapting to conditions. He also highlights the importance of harmony between body, mind, and spirit, crucial for achieving mastery in martial arts and in life.
 Water: Flexibility and Adaptation In "The Book of Water," Musashi focuses on flexibility and the ability to adapt, just as water conforms to the shape of its container. This part presents dynamic and fluid combat techniques and stances. It addresses tactics, the rhythm of combat, and the importance of intuition, emphasizing that a true warrior must be able to quickly adapt to changing circumstances.
Water: Flexibility and Adaptation In "The Book of Water," Musashi focuses on flexibility and the ability to adapt, just as water conforms to the shape of its container. This part presents dynamic and fluid combat techniques and stances. It addresses tactics, the rhythm of combat, and the importance of intuition, emphasizing that a true warrior must be able to quickly adapt to changing circumstances.

 Wind: Understanding the Opponent In "The Book of Wind," Musashi focuses on the importance of understanding the styles and techniques of opponents. He compares this to the wind, which brings information and allows one to anticipate an opponent's moves. This part is dedicated to analyzing and understanding various swordsmanship schools and methods of overcoming them, reflecting Musashi's deep understanding of a broad spectrum of combat strategies.
Wind: Understanding the Opponent In "The Book of Wind," Musashi focuses on the importance of understanding the styles and techniques of opponents. He compares this to the wind, which brings information and allows one to anticipate an opponent's moves. This part is dedicated to analyzing and understanding various swordsmanship schools and methods of overcoming them, reflecting Musashi's deep understanding of a broad spectrum of combat strategies.
 Void: The Essence of Strategy The final part, "The Book of Void," is the most abstract and philosophical. Here, Musashi speaks of the state of "void" – a state of mind free from distractions, fears, and false thoughts. The void is not an absence but rather a place of infinite possibilities, a state where a warrior is fully aware and ready to act. Musashi emphasizes that achieving this state allows one to reach the highest form of mastery, both in martial arts and in life.
Void: The Essence of Strategy The final part, "The Book of Void," is the most abstract and philosophical. Here, Musashi speaks of the state of "void" – a state of mind free from distractions, fears, and false thoughts. The void is not an absence but rather a place of infinite possibilities, a state where a warrior is fully aware and ready to act. Musashi emphasizes that achieving this state allows one to reach the highest form of mastery, both in martial arts and in life.
 Impact of "The Book of Five Rings" on Asian Culture
Impact of "The Book of Five Rings" on Asian Culture
"The Book of Five Rings" by Miyamoto Musashi has had an invaluable impact on Japanese culture and martial arts worldwide. Its principles of strategy and philosophy have found application not only in traditional Japanese swordsmanship schools but also in modern forms of combat and martial arts, such as kendo, judo, and aikido. Beyond martial arts, the principles outlined by Musashi have been adapted in various life areas, from business to management and psychology. In Japan, the book is often cited as a source of inspiration for leaders and entrepreneurs, emphasizing the importance of adaptation, intuition, and strategic thinking. In literature and film, "The Book of Five Rings" has been interpreted and adapted multiple times, highlighting its lasting impact on Japanese culture.
Internationally, "The Book of Five Rings" has gained recognition as a classic of military and strategic literature, comparable to Sun Tzu's "The Art of War." Its translations and interpretations have appeared in many languages, inspiring readers worldwide. Musashi's approach to combat, based on understanding the nature of the mind and body, has attracted the interest of psychologists and personal development practitioners, testifying to the universality and timelessness of his teachings.
 The Remaining Works of Miyamoto Musashi
The Remaining Works of Miyamoto Musashi
Beyond "The Book of Five Rings," Miyamoto Musashi was also a recognized artist and calligrapher. His calligraphy works are characterized by a dynamic style and depth of expression, reflecting his life and combat philosophy. His paintings, often depicting natural scenes such as birds, trees, and landscapes, are valued for their simplicity and depth. These artworks were expressions of his understanding of the Zen path and harmony with nature. Musashi explored the ideas of void and balance in them, which were key elements of his life philosophy.
Musashi also wrote other treatises and texts, including "The Path of Aloneness" (Dokkōdō), containing his final thoughts on life and philosophy. This short text, consisting of 21 precepts, was written just before his death in 1645 and is considered his spiritual testament. In these precepts, Musashi emphasizes the importance of self-discipline, personal independence, and inner peace. His works, both literary and artistic, are still valued for their depth and the impact they have had on Japanese culture and art.
Musashi's Legacy in Contemporary Culture
Musashi in Anime and Manga
"Vagabond" is a manga offering a fictionalized portrayal of Musashi's life, based on Eiji Yoshikawa's novel. This epic story, blending historical facts with fiction, depicts Musashi's journey from a wild youth to a master swordsman and philosopher. The manga highlights Musashi's character development, his combat techniques, and spiritual journey.
 "Onimusha" is an anime that tells the adventures of Musashi, portraying him as a legendary warrior. Although loosely based on the historical Musashi, the series presents him as an iconic samurai figure, exploring various aspects of his life and legend.
"Onimusha" is an anime that tells the adventures of Musashi, portraying him as a legendary warrior. Although loosely based on the historical Musashi, the series presents him as an iconic samurai figure, exploring various aspects of his life and legend.
In the anime "Miyamoto Musashi: Souken ni Haseru Yume," we see a story of Musashi's life, from his early years to his famous duels. The anime emphasizes the significance of his combat techniques and philosophical approach to life, influencing subsequent generations of warriors.
"Shura no Toki – Age of Chaos" portrays Musashi in the context of his combat skills and confrontations with other martial arts masters. This anime series explores different aspects of his fighting style and shows how his techniques were used in various historical periods.
 In the "Pokémon" series, the character Musashi (known as Jessie in the English version), a member of Team Rocket, is named after Miyamoto Musashi. Although this character has little in common with the historical samurai, her name is a tribute to his enduring impact on Japanese culture.
In the "Pokémon" series, the character Musashi (known as Jessie in the English version), a member of Team Rocket, is named after Miyamoto Musashi. Although this character has little in common with the historical samurai, her name is a tribute to his enduring impact on Japanese culture.
The Influence of Musashi's Character on Video Games
 "Ganryu 2" is a 2D platform game where the player takes on the role of Musashi, traveling through 17th-century Japan. The game draws from the tales of Musashi, highlighting his legendary duels and sword fighting skills.
"Ganryu 2" is a 2D platform game where the player takes on the role of Musashi, traveling through 17th-century Japan. The game draws from the tales of Musashi, highlighting his legendary duels and sword fighting skills.
"Ganryu", released in 1999, is a hack-and-slash game loosely based on Musashi's duel with Sasaki Kojirō. The game reflects elements of this historical battle, showcasing Musashi as an iconic warrior.
The "Brave Fencer Musashi" and "Musashi: Samurai Legend" series on PlayStation feature adventures of Musashi in a fictional world, where he uses two swords and faces a rival reminiscent of his historical encounter with Kojirō. These games combine fantasy elements with inspirations drawn from Musashi's life and legend.
 "Musashi no Bōken" is a 1990 Family Computer game that introduces players to adventures inspired by Musashi, though in a more humorous and fantastical form.
"Musashi no Bōken" is a 1990 Family Computer game that introduces players to adventures inspired by Musashi, though in a more humorous and fantastical form.
In the game "League of Legends", the character Yasuo is loosely based on Musashi, reflecting his fighting style and philosophy. Yasuo, a wandering warrior with a past full of conflicts, resembles Musashi's own life journey and quest for redemption.
Musashi as a Symbol and Icon in Films and Other Media
"Samurai I: Musashi Miyamoto" (1954), directed by Hiroshi Inagaki, is the first part of the "Samurai" trilogy, starring Toshiro Mifune as Musashi. The film portrays his transformation from a young, wild warrior to a mature samurai, highlighting both his combat skills and spiritual evolution.
"Sorekara no Musashi", a TV series from 1964-65, depicts Musashi's life leading up to his legendary duel with Sasaki Kojirō. The series offers a deeper look into Musashi's life, blending historical elements with dramatic storytelling.
"MUSASHI" (2003), an NHK taiga drama* based mainly on Yoshikawa's novel, features kabuki actor Ichikawa Ebizō XI as Musashi. This TV drama explores various aspects of Musashi's life, from his early years to his famous duels and transformation into a philosopher.
"Crazy Samurai Musashi" (2020), directed by Yūji Shimomura, presents Musashi as an undefeated samurai, focusing on his combat skills and legendary duels.
In the American TV series "Westworld" (2018), Musashi appears as a "host" in the Shogun World theme park. This adaptation portrays him as both a mystical and powerful figure, combining traditional elements with a modern perspective on the samurai legend.
Conclusion

An interesting fact about Musashi is that, despite being known as an undefeated warrior, he never served any ruling daimyō, a rarity among samurais of his time. Another intriguing aspect is his interest in agriculture later in life; Musashi became renowned as an expert in this field, an unexpected occupation for someone who spent his life perfecting the art of combat. These facets of Musashi's life highlight his complex personality and versatility, and his legacy remains a significant and enduring element of not only Japanese history but also global culture.
*A "taiga drama" is a term used in Japan to describe a genre of long, historical TV dramas produced by the Japanese public broadcaster NHK. These series are known for their elaborate plots that narrate important events or figures in Japanese history. They feature high budgets, meticulous set and costume designs that accurately depict historical periods. "Taiga dramas" are broadcasted weekly throughout the year, with each episode lasting about 45 minutes. Due to their quality and popularity, these series significantly influence public perception of Japanese history.
"Strong Japanese Women"
see book by the author
of the page
未開 ソビエライ
An enthusiast of Asian culture with a deep appreciation for the diverse philosophies of the world. By education, a psychologist and philologist specializing in Korean studies. At heart, a programmer (primarily for Android) and a passionate technology enthusiast, as well as a practitioner of Zen and mono no aware. In moments of tranquility, adheres to a disciplined lifestyle, firmly believing that perseverance, continuous personal growth, and dedication to one's passions are the wisest paths in life. Author of the book "Strong Women of Japan" (>>see more)
Personal motto:
"The most powerful force in the universe is compound interest." - Albert Einstein (probably)
Mike Soray
(aka Michał Sobieraj)
未開 ソビエライ
An enthusiast of Asian culture with a deep appreciation for the diverse philosophies of the world. By education, a psychologist and philologist specializing in Korean studies. At heart, a programmer (primarily for Android) and a passionate technology enthusiast, as well as a practitioner of Zen and mono no aware. In moments of tranquility, adheres to a disciplined lifestyle, firmly believing that perseverance, continuous personal growth, and dedication to one's passions are the wisest paths in life. Author of the book "Strong Women of Japan" (>>see more)
Personal motto:
"The most powerful force in the universe is compound interest." - Albert Einstein (probably)
Mike Soray
(aka Michał Sobieraj)
Write us...
Ciechanów, Polska
dr.imyon@gmail.com
___________________
inari.smart
Would you like to share your thoughts or feedback about our website or app? Leave us a message, and we’ll get back to you quickly. We value your perspective!
 Miyamoto Musashi: The Unparalleled Master of Samurai Art
Miyamoto Musashi: The Unparalleled Master of Samurai Art  Key Moments in His Samurai Career - Youth
Key Moments in His Samurai Career - Youth  Significant Duels and Battles
Significant Duels and Battles Duel of Strength and Cunning – Sasaki Kojirō
Duel of Strength and Cunning – Sasaki Kojirō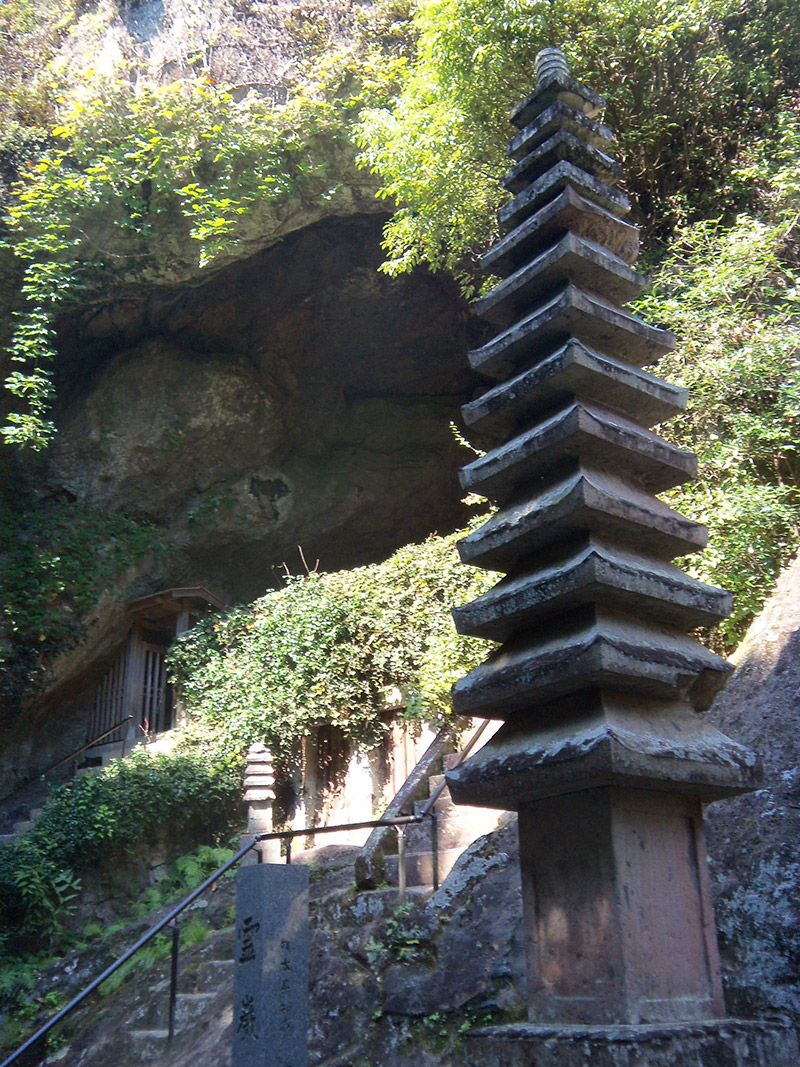 The Transformation from Warrior to Philosopher
The Transformation from Warrior to Philosopher Earth: The Foundations of Strategy The first part, "The Book of Earth," lays the foundation for the rest. Musashi discusses the basics of strategy and combat, emphasizing the importance of stability, understanding one's environment, and adapting to conditions. He also highlights the importance of harmony between body, mind, and spirit, crucial for achieving mastery in martial arts and in life.
Earth: The Foundations of Strategy The first part, "The Book of Earth," lays the foundation for the rest. Musashi discusses the basics of strategy and combat, emphasizing the importance of stability, understanding one's environment, and adapting to conditions. He also highlights the importance of harmony between body, mind, and spirit, crucial for achieving mastery in martial arts and in life. Water: Flexibility and Adaptation In "The Book of Water," Musashi focuses on flexibility and the ability to adapt, just as water conforms to the shape of its container. This part presents dynamic and fluid combat techniques and stances. It addresses tactics, the rhythm of combat, and the importance of intuition, emphasizing that a true warrior must be able to quickly adapt to changing circumstances.
Water: Flexibility and Adaptation In "The Book of Water," Musashi focuses on flexibility and the ability to adapt, just as water conforms to the shape of its container. This part presents dynamic and fluid combat techniques and stances. It addresses tactics, the rhythm of combat, and the importance of intuition, emphasizing that a true warrior must be able to quickly adapt to changing circumstances. Wind: Understanding the Opponent In "The Book of Wind," Musashi focuses on the importance of understanding the styles and techniques of opponents. He compares this to the wind, which brings information and allows one to anticipate an opponent's moves. This part is dedicated to analyzing and understanding various swordsmanship schools and methods of overcoming them, reflecting Musashi's deep understanding of a broad spectrum of combat strategies.
Wind: Understanding the Opponent In "The Book of Wind," Musashi focuses on the importance of understanding the styles and techniques of opponents. He compares this to the wind, which brings information and allows one to anticipate an opponent's moves. This part is dedicated to analyzing and understanding various swordsmanship schools and methods of overcoming them, reflecting Musashi's deep understanding of a broad spectrum of combat strategies. Void: The Essence of Strategy The final part, "The Book of Void," is the most abstract and philosophical. Here, Musashi speaks of the state of "void" – a state of mind free from distractions, fears, and false thoughts. The void is not an absence but rather a place of infinite possibilities, a state where a warrior is fully aware and ready to act. Musashi emphasizes that achieving this state allows one to reach the highest form of mastery, both in martial arts and in life.
Void: The Essence of Strategy The final part, "The Book of Void," is the most abstract and philosophical. Here, Musashi speaks of the state of "void" – a state of mind free from distractions, fears, and false thoughts. The void is not an absence but rather a place of infinite possibilities, a state where a warrior is fully aware and ready to act. Musashi emphasizes that achieving this state allows one to reach the highest form of mastery, both in martial arts and in life. Impact of "The Book of Five Rings" on Asian Culture
Impact of "The Book of Five Rings" on Asian Culture The Remaining Works of Miyamoto Musashi
The Remaining Works of Miyamoto Musashi "Onimusha" is an anime that tells the adventures of Musashi, portraying him as a legendary warrior. Although loosely based on the historical Musashi, the series presents him as an iconic samurai figure, exploring various aspects of his life and legend.
"Onimusha" is an anime that tells the adventures of Musashi, portraying him as a legendary warrior. Although loosely based on the historical Musashi, the series presents him as an iconic samurai figure, exploring various aspects of his life and legend. In the "Pokémon" series, the character Musashi (known as Jessie in the English version), a member of Team Rocket, is named after Miyamoto Musashi. Although this character has little in common with the historical samurai, her name is a tribute to his enduring impact on Japanese culture.
In the "Pokémon" series, the character Musashi (known as Jessie in the English version), a member of Team Rocket, is named after Miyamoto Musashi. Although this character has little in common with the historical samurai, her name is a tribute to his enduring impact on Japanese culture. "Ganryu 2" is a 2D platform game where the player takes on the role of Musashi, traveling through 17th-century Japan. The game draws from the tales of Musashi, highlighting his legendary duels and sword fighting skills.
"Ganryu 2" is a 2D platform game where the player takes on the role of Musashi, traveling through 17th-century Japan. The game draws from the tales of Musashi, highlighting his legendary duels and sword fighting skills. "Musashi no Bōken" is a 1990 Family Computer game that introduces players to adventures inspired by Musashi, though in a more humorous and fantastical form.
"Musashi no Bōken" is a 1990 Family Computer game that introduces players to adventures inspired by Musashi, though in a more humorous and fantastical form.



